Traveling Luck for Aland Islands. Aland Islands, Europe
Finland is located in Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, and Gulf of Finland, between Sweden and Russia.
Land in Finland is mostly low, flat to rolling plains interspersed with lakes and low hills.
Finnish land covers an area of 338145 square kilometers which is slightly smaller than Montana
Aland Islands has borders with Norway for 727km, Russia for 1340km and Sweden for 614km.
 Finnish national flag (Flag of Aland Islands)
Finnish national flag (Flag of Aland Islands)
As for the Finnish climate; cold temperate; potentially subarctic but comparatively mild because of moderating influence of the North Atlantic Current, Baltic Sea, and more than 60,000 lakes.
Finn(s) speak Finnish 92% (official), Swedish 5.6% (official), other 2.4% (small Sami- and Russian-speaking minorities) (2003).
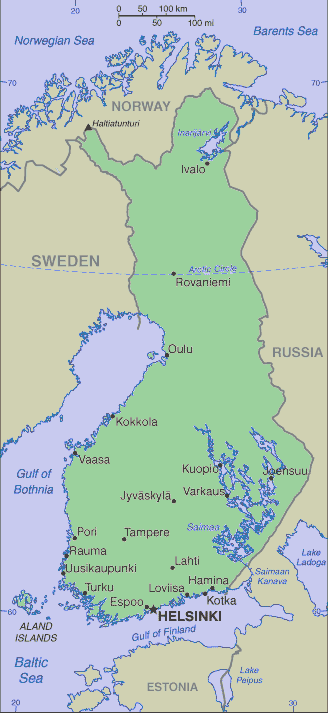 Finnish map
Finnish map
Regions of Aland Islands
Finland was a province and then a grand duchy under Sweden from the 12th to the 19th centuries and an autonomous grand duchy of Russia after 1809. It won its complete independence in 1917. During World War II, it was able to successfully defend its freedom and resist invasions by the Soviet Union - albeit with some loss of territory. In the subsequent half century, the Finns made a remarkable transformation from a farm/forest economy to a diversified modern industrial economy; per capita income is now on par with Western Europe. As a member of the European Union, Finland was the only Nordic state to join the euro system at its initiation in January 1999.
Finland has a highly industrialized, largely free-market economy with per capita output roughly that of the UK, France, Germany, and Italy. Its key economic sector is manufacturing - principally the wood, metals, engineering, telecommunications, and electronics industries. Trade is important; exports equal two-fifths of GDP. Finland excels in high-tech exports, e.g., mobile phones. Except for timber and several minerals, Finland depends on imports of raw materials, energy, and some components for manufactured goods. Because of the climate, agricultural development is limited to maintaining self-sufficiency in basic products. Forestry, an important export earner, provides a secondary occupation for the rural population. Rapidly increasing integration with Western Europe - Finland was one of the 12 countries joining the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) - will dominate the economic picture over the next several years. High unemployment remains a persistent problem.
Finnish natural resources include timber, iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, chromite, nickel, gold, silver, limestone
long boundary with Russia; Helsinki is northernmost national capital on European continent; population concentrated on small southwestern coastal plain
Finnish religion is Lutheran National Church 84.2%, Greek Orthodox in Finland 1.1%, other Christian 1.1%, other 0.1%, none 13.5% (2003).
Natural hazards in Finland include NA.

 Search
Search